Note: I had to use PUBS to do this practice...
Select tables
USE
PUBS
--'--
THE BASICS (Level 1) ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------'
SELECT * FROM Publishers
SELECT * FROM Titles
CROSS JOINS
--'***
The "Old" way of doing JOINS (ANSI 89)
"new way in yellow" ***'
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-- Cross
Join --
SELECT
Title, Pub_name
FROM
Titles, Publishers
-- Cross Join --
Select Title, Pub_name
From Titles cross Join Publishers
INNER JOIN
-- Inner
Join --
-- an
inner join to retrieve data from the Publishers table and the Titles table in
the Pubs database:
SELECT
Title, Pub_name
FROM
Titles AS T,
Publishers
WHERE T.Pub_id = Publishers.Pub_id
-- Inner Join --
Select T.Title, Pub_name,
Pub_Id
From Titles T
Inner Join Publishers On T.Pub_id = Publishers.Pub_id
OUTER JOIN
-- Outer
Join --
SELECT
Title, Pub_name
FROM
Titles, Publishers
WHERE
Titles.Pub_id =
Publishers.Pub_id
AND
Pub_name LIKE 'A%'
-- Outer Join --
Select Title, Pub_name
From Titles
Right Outer Join Publishers On Titles.Pub_id = Publishers.Pub_id
Where Pub_name like 'A%'
SELECT TABLES
'*** A
Self Join Example ***'
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Use
Northwind
Select
ReportsTo, *
From
Employees
A Self Join Example
Select
E.FirstName + ' ' + E.LastName as 'Emp Name',
M.FirstName + ' ' + M.LastName as 'Mgr Name'
From
Employees as E,
Employees as M
Where E.ReportsTo = M.EmployeeId
Select
E.FirstName + ' ' + E.LastName as 'Emp Name',
M.FirstName + ' ' + M.LastName as 'Mgr Name'
From
Employees as E Join
Employees as M
On E.ReportsTo = M.EmployeeId
LAB 1: CREATE A REPORT
'********************
LAB ***********************'
-- Do
the following:
-- 1)
Use the Northwind datebase to produce a
-- Report
that shows a list of Categories and
-- Products
'*************************************************'
Answer:
Select reverse(' emaNyrogetaC.C yB
redrO DIyrogetaC.P = DIyrogetaC.C
erehW P sa stcudorP.obd ,C sa
seirogetaC.obd morf emaNtcudorP.P
,emaNyrogetaC.C tceleS ')
Joining more than One Table
USE
Pubs
SELECT
au_fname + ' ' + au_lname AS 'Authors Name',
title as 'Title of Book',
pub_name
AS 'Publishers
Name'
FROM
authors,
titleauthor,
titles,
publishers
WHERE
Authors.Au_Id = TitleAuthor.Au_id
AND
TitleAuthor.Title_id
= Titles.Title_id
AND
Titles.Pub_Id = Publishers.Pub_id
-- Same as above but using the ANSI
syntax
SELECT
au_fname + ' ' +
au_lname AS 'Authors Name',
title AS 'Title of Book',
pub_name AS 'Publishers Name'
FROM authors
JOIN titleauthor ON Authors.Au_Id = TitleAuthor.Au_id
JOIN titles ON TitleAuthor.Title_id = Titles.Title_id
JOIN publishers ON Titles.Pub_Id = Publishers.Pub_id
Left /Right/Full JOINS
LEFT
-- a
left outer join is used to retrieve the authors first names, last names, and
(when applicable)
-- the
names of any publishers that are located in the same cities as the authors:
USE
Pubs
SELECT a.Au_fname, a.Au_lname, p.Pub_name
FROM
Authors a
LEFT OUTER
JOIN Publishers p ON a.City = p.City
ORDER BY p.Pub_name ASC, a.Au_lname ASC, a.Au_fname ASC
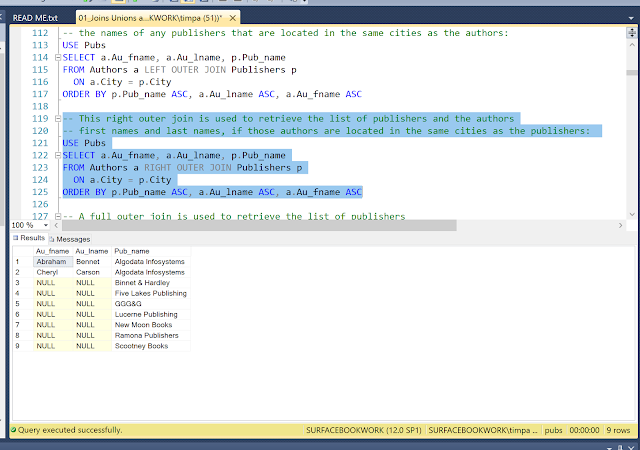
RIGHT
-- This
right outer join is used to retrieve the list of publishers and the authors
-- first
names and last names, if those authors are located in the same cities as the
publishers:
USE
Pubs
SELECT a.Au_fname, a.Au_lname, p.Pub_name
FROM
Authors a
RIGHT OUTER
JOIN Publishers p ON a.City = p.City
ORDER BY p.Pub_name ASC, a.Au_lname ASC, a.Au_fname ASC
FULL
-- A
full outer join is used to retrieve the list of publishers
-- and
authors' first and last names:
USE
Pubs
SELECT a.Au_fname, a.Au_lname, p.Pub_name
FROM
Authors a
FULL OUTER
JOIN Publishers p ON a.City = p.City
ORDER BY p.Pub_name ASC, a.Au_lname ASC, a.Au_fname ASC
Cross Join behaves as an Inner Join
-- If a
WHERE clause is added, the cross join behaves as an inner join.
USE
pubs
SELECT
au_fname, au_lname,
pub_name
FROM
authors
CROSS JOIN publishers
WHERE
authors.city =
publishers.city
ORDER BY au_lname DESC
-- Is
the same as:
USE
pubs
SELECT
au_fname, au_lname,
pub_name
FROM
authors
INNER JOIN publishers ON
authors.city =
publishers.city
ORDER BY au_lname DESC









No comments:
Post a Comment